THEOREMS ON CIRCLES
Angles Subtended at the Arc
Theorem :
When two angles subtended by the same arc, the angle at the center of the circle is twice the angle at the circumference.
Proof :
Considering the circle with center O, now placing the points A, B and C on the circumference.
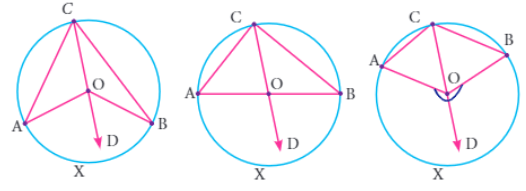
∠ACO = ∠OAC
∠BCO = ∠OBC
∠AOD = Exterior angle of the triangle
∠AOD = ∠ACO + ∠OAC ----(1)
∠BOD = ∠BCO + ∠OBC ----(2)
(1) + (2)
∠AOD + ∠BOD = (∠ACO + ∠OAC) + (∠BCO + ∠OBC)
∠AOB = (∠ACO + ∠OAC) + (∠BCO + ∠OBC)
∠AOB = 2∠OCA + 2∠OCB
∠AOB = 2(∠OCA + ∠OCB)
∠AOB = 2∠ACB
Related Pages
Angles on the Same Segment
Angles subtended by the same arc at the circumference are equal. This means that angles in the same segment are equal
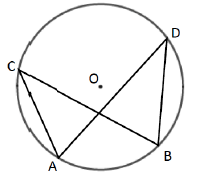
∠ACB = ∠ADB
Related Pages
Line Drawn from the Center to Tangent
A tangent is a straight line that touches the circumference of a circle at only one point. The angle between a tangent and the radius is 90˚.
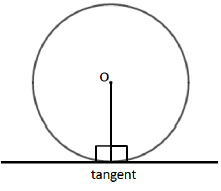
- The line which is drawn from the center of the circle to tangent of that circle is simply known as the radius of that circle.
- The radius will be perpendicular on the tangent in this case.
- The radius is the half of the diameter of the same circle.
Related Pages
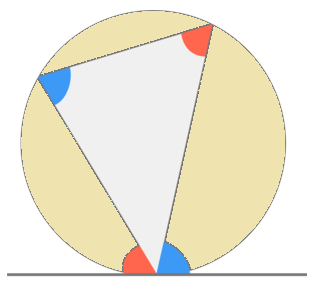
Alternate Segment Theorem
In any circle, the angle between a chord and a tangent through one of the end points of the chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment.
Related Pages
Angle in Semicircle
The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
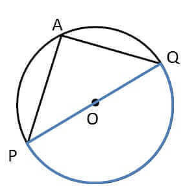
∠POQ = 180
2∠PAQ = ∠POQ
2∠PAQ = 180
∠PAQ = 180/2
∠PAQ = 90
Related Pages
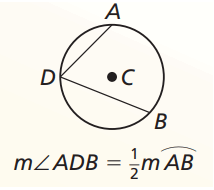
Inscribed Angle Intercepted Arc of the Circle
What is inscribed angle ?
Angle whose vertex is on the circle ang whose sides are chords of a circle.
Intercepted arc ?
The arc that lies between two chords on the inscribed angle.
Measure of an inscribed angle is half of its intercepted arc.
Related Pages
Cyclic Quadrilateral and Intercepted Arc
A cyclic quadrilateral is a quadrilateral which has all its four vertices lying on a circle. It is also sometimes called inscribed quadrilateral.
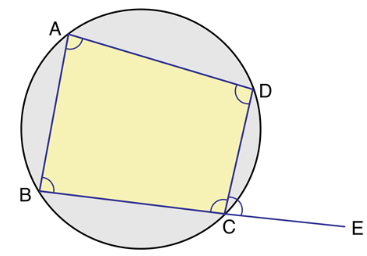
In which opposite angles are supplementary.
Exterior angle is equal to opposite interior angle. That is, in the above cyclic quadrilateral
∠DCE = ∠BAD
Related Pages
Intersecting Chords
If two chords intersect inside a circle, then the measure of each angle formed is one half the sum of the measures of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle.
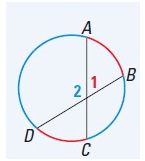
m∠1 = 1/2(mCD + mAB),
m∠2 = 1/2(mAD + mBC)
Related Pages
Intersecting Secants Theorem
The measure of an angle formed by two secants, a secant and a tangent, or two tangents intersecting in the exterior of a circle is equal to one-half the positive difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
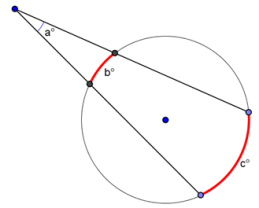
Related Pages
Secants Intersecting Outside of Circle
AH and HY are the two secant segments intersecting at point H. SH is the external secant segment of the whole secant segment AH, and LH is the external secant segment of HY. Thus, according to the theorem, we have
SH × AH = HL × HY
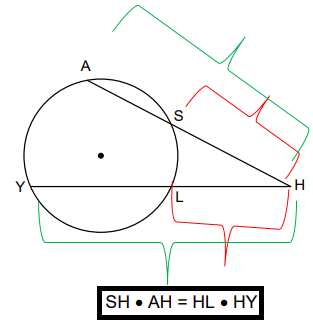
Related Pages
Chord Chord Product Theorem
The products of the lengths of the line segments on each chord are equal.
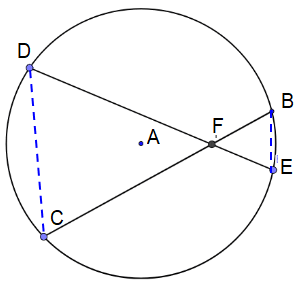
CF ⋅ BF = DF ⋅ EF
Related Pages
Secant Tangent Product Theorem
If a secant and tangent share a point then the product of the secant and external part is equal to tangent squared.
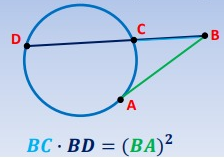
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling