SOLVING ABSOLUTE VALUE INEQUALITIES GRAPHICALLY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
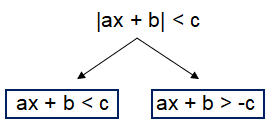
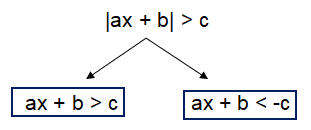
The absolute value inequality which is in the form of
|ax + b| < c, |ax + b| ≤ c, |ax + b| > c or |ax + b| ≥ c
can be decomposed into two branches.
 |
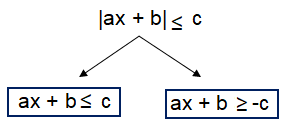 |
 |
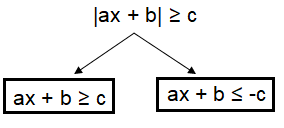 |
Then we will solve those two branches separately and find the values of unknown.
To represent the solution in the number line, we will use two types of circles.
- Solid circle (or) filled circle
- Transparent circle (or) empty circle
In the inequality, if we have ≥ or ≤ then we have to use solid circle.
In the inequality, if we have < or > then we have to use empty circle.
Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution.
Problem 1 :
|d + 4| ≥ 3
Solution :
|d + 4| ≥ 3
|
d + 4 ≥ 3 d ≥ 3 – 4 d ≥ -1 |
d + 4 ≤ -3 d ≤ -3 - 4 d ≤ -7 |
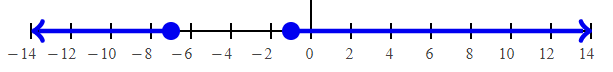
Converting into interval notation, we get
(-∞, -7] U [-1, ∞)
Problem 2 :
|f + 6| < 2
Solution :
|f + 6| < 2
|
f + 6 < 2 f < 2 – 6 f < -4 |
f + 6 > -2 f > -2 – 6 f > -8 |
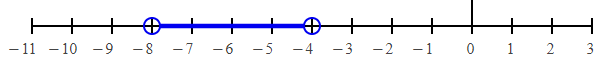
Converting the shaded portion as interval notation, we get
(-8, -4)
Problem 3 :
|3w - 15| < 30
Solution :
|3w - 15| < 30
|
3w - 15 < 30 3w < 30 + 15 3w < 45 w < 45/3 w < 15 |
3w - 15 > -30 3w > -30 + 15 3w > -15 w > -15/3 w > -5 |
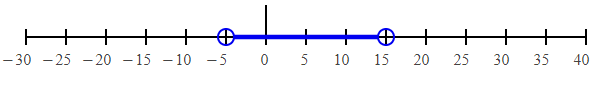
Converting the shaded region as interval notation, we get
(-5, 15).
Problem 4 :
|2x + 6| ≥ 10
Solution :
|2x + 6| ≥ 10
|
2x + 6 ≥ 10 2x ≥ 10 – 6 2x ≥ 4 x ≥ 4/2 x ≥ 2 |
2x + 6 ≤ -10 2x ≤ -10 – 6 2x ≤ -16 x ≤ -16/2 x ≤ -8 |
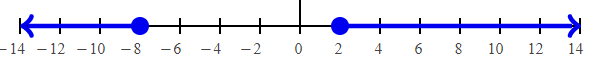
Converting into interval notation, we get
(-∞, -8] U [2, ∞)
Problem 5 :
|16 - p| > 3
Solution :
|16 - p| > 3
|
16 - p > 3 - p > 3 – 16 -p > -13 p > 13 |
16 - p < -3 -p < -3 – 16 -p < -19 p < 19 |
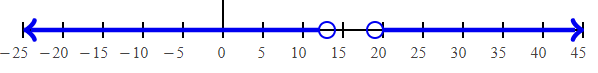
Converting into interval notation, we get
(-∞, 13) U [19, ∞)
Problem 6 :
|24 - q| ≤ 11
Solution :
|24 - q| ≤ 11
|
24 - q ≤ 11 -q ≤ 11 – 24 -q ≤ -13 q ≤ 13 |
24 – q ≥ -11 -q ≥ -11 – 24 -q ≥ -35 q ≥ 35 |
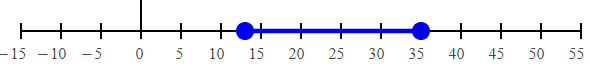
Converting into interval notation, we get
(13, 35]
Problem 7 :
|1/2x - 10| ≤ 4
Solution :
|1/2x - 10| ≤ 4
|
1/2x – 10 ≤ 4 1/2x ≤ 4 + 10 1/2x ≤ 14 x ≤ 14 × 2 x ≤ 28 |
1/2x – 10 ≥ -4 1/2x ≥ -4 + 10 1/2x ≥ 6 x ≥ 6 × 2 x ≥ 12 |
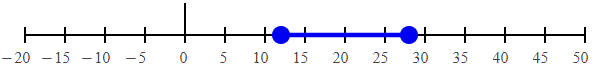
Converting into interval notation, we get
[12, 28]
Problem 8 :
|(1/3)m - 15| < 6
Solution :
|(1/3)m - 15| < 6
|
(1/3)m - 15 < 6 (1/3)m < 6 + 15 (1/3)m < 21 m < 21 × 3 m < 63 |
(1/3)m - 15 > -6 (1/3)m > -6 + 15 (1/3)m > 9 m > 9 ×3 m > 27 |
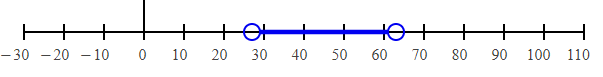
Converting into interval notation, we get
(27, 63)
Problem 9 :
|(1/7)y + 2| - 5 > 3
Solution :
|(1/7)y + 2| - 5 > 3
|(1/7)y + 2| > 3 + 5
|
|(1/7)y + 2| > 8 (1/7)y + 2 > 8 (1/7)y > 8 – 2 (1/7)y > 6 y > 6 × 7 y > 42 |
(1/7)y + 2 < -8 (1/7)y < -8 – 2 (1/7)y < -10 y < -10 × 7 y < -70 |
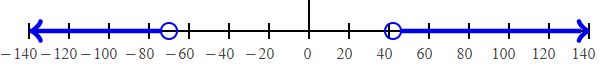
Converting into interval notation, we get
(-∞, -70) U (42, ∞)
Problem 10 :
|(2/5)n - 8| + 4 ≥ 12
Solution :
|2/5n - 8| + 4 ≥ 12
|2/5n – 8| ≥ 12 - 4
|2/5n – 8| ≥ 8
|
(2/5)n – 8 ≥ 8 (2/5)n ≥ 8 + 8 (2/5)n ≥ 16 n ≥ 16 × 5/2 n ≥ 40 |
(2/5)n – 8 ≤ -8 (2/5)n ≤ -8 + 8 (2/5)n ≤ 0 n ≤ 0 |
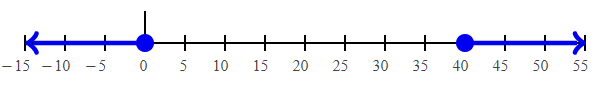
Converting into interval notation, we get
(-∞, 0] U [40, ∞)
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling