SEGMENT SEGMENT PRODUCT THEOREM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
If two
secants intersect in the exterior of a circle, then the product of the measures
of one secant segment and its external secant segments is equal to the product
of the measures of the other secant and its external secant segment.
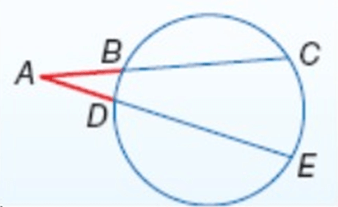
AC ∙ AB = AE ∙ AD
Find x.
Problem 1:
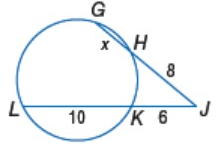
Solution :
Using theorem,
JH ∙ JG = JK ∙ JL
8 ∙ (8 + x) = 6 ∙ (6 + 10)
64 + 8x = 96
8x = 32
x = 32/8
x = 4
Problem 2 :
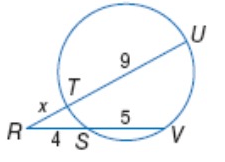
Solution :
Using theorem,
RT ∙ RU = RS ∙ RV
x ∙ (x + 9) = 4 ∙ (4 + 5)
x² + 9x = 36
x² + 9x - 36 = 0
(x + 12) (x - 3) = 0
x = -12 or x = 3
We can use only positive value for x. because lengths cannot be negative.
So, we have
x = 3
Problem 3 :
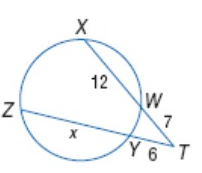
Solution :
Using theorem,
TW ∙ TX = TY ∙ TZ
7 ∙ (7 + 12) = 6 ∙ (6 + x)
133 = 36 + 6x
6x = 97
x = 97/6
x ≈ 16
For each figure, determine the value of the variable and the indicated lengths by applying the Secant-Secant product theorem.
Problem 4 :
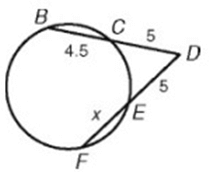
Solution :
DC ∙ DB = DE ∙ DF
5 ∙ (5 + 4.5) = 5 ∙ (5 + x)
47.5 = 25 + 5x
5x = 47.5 - 25
5x = 22.5
x = 4.5
|
BD = BC + CD = 4.5 + 5 BD = 9.5 |
FD = FE + ED = x + 5 = 4.5 + 5 FD = 9.5 |
Problem 5 :
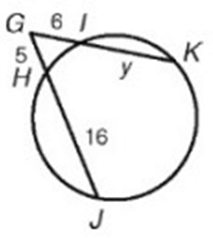
Solution :
Using theorem,
GI ∙ GK = GH ∙ GJ
6 ∙ (6 + y) = 5 ∙ (5 + 16)
36 + 6y = 105
6y = 105 - 36
6y = 69
y = 11.5
|
GJ = GH + HJ = 5 + 16 GJ = 21 |
GK = GI + IK = 6 + y = 6 + 11.5 GK = 17.5 |
Problem 6 :
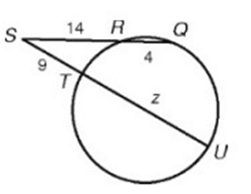
Solution :
Using theorem,
SR ∙ SQ = ST ∙ SU
14 ∙ (14 + 4) = 9 ∙ (9 + z)
252 = 81 + 9z
9z = 252 - 81
9z = 171
z = 19
|
SQ = SR + RQ = 14 + 4 SQ = 18 |
SU = ST + TU = 9 + z = 9 + 19 SU = 28 |
Problem 7:
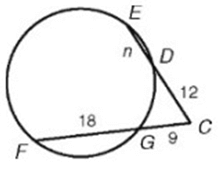
Solution :
Using theorem,
CD ∙ CE = CG ∙ CF
12 ∙ (12 + n) = 9 ∙ (9 + 18)
144 + 12n = 243
12n = 243 - 144
12n = 99
n = 8.25
|
CE = CD + DE = 12 + n = 12 + 8.25 CE = 20.25 |
CF = CG + GF = 9 + 18 CF = 27 |
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling