REPRESENTING SAMPLE SPACES IN DIFFERENT WAYS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
Possible ways of representing sample space are :
a) Listing them
b) Using a dimensional grid
c) Using tree diagram
d) Using venn diagram
Problem 1 :
Represent the sample space for tossing two coins using
a) a list
b) 2-D grid
c) a tree diagram
Solution :
In every coin, we see two faces. Head and tail.
Let H be the head and T be the tail.
a) a list
S = {HH, TT, HT, TH}
b) 2-D grid
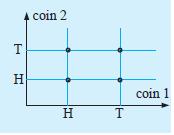
c) tree diagram
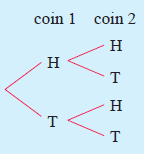
Problem 2 :
Illustrate, using tree diagram, the possible outcomes when drawing two marbles from a bag containing several marbles of each of the colors, red green and yellow.
Solution :
Let R be the red marble
G be the green marble and
Y be the yellow marble.
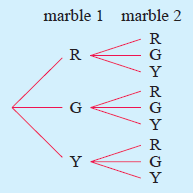
List the sample space for the following.
Problem 3 :
Twirling a square spinner labelled A, B , C and D.
Solution :
Sample space = {A, B, C, D}
Problem 4 :
The sexes of a 2 child family.
Solution :
Let B be the boy child and G be the girl child.
Sample space = {GG, BB, GB, BG}
Problem 5 :
The order in which 4 blocks A, B, C and D can be lined up.
Solution :
Keeping A first,
ABCD, ABDC, ACBD, ACDB, ADBC, ADCB
Keeping B first
BACD, BADC, BCDA, BCAD, BDAC, BDCA
Keeping C first
CABD, CADB, CBDA, CBAD, CDAB, CDBA
Keeping D first
DABC, DACB, DBAC, DBCA, DCAB, DCBA
Sample space
= {ABCD, ABDC, ACBD, ACDB, ADBC, ADCB, BACD, BADC, BCDA, BCAD, BDAC, BDCA, CABD, CADB, CBDA, CBAD, CDAB, CDBA, DABC, DACB, DBAC, DBCA, DCAB, DCBA}
Problem 6 :
The 8 different 3 child families.
Solution :
Let G b be the girl child and B be the boy child.
Sample space = {GGG, BBB, GGB, GBG, BGG, BBG, BGB, GBB}
Problem 7 :
Spinning a coin :
i) twice ii) three times iii) four times
Solution :
Let H be the head and T be the tail.
a) A coin is spinning twice
Sample space = {HH, TT, HT, TH}
b) A coin is spinning three times
Sample space = {HHH, TTT, HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, THT, HTT}
c) A coin is spinning four times
Sample space = {HHHH, TTTT, HHHT, HHTH, HTHH, THHH, HHTT, HTTH, TTHH, THTH, HTTT, THTT, TTHT, TTTH, HHHT, HTTT }
Illustrate on a 2 dimensional grid the sample space for :
Problem 8 :
A rolling a die and tossing a coin simultaneously
Solution :
- When rolling a coin, we will get two outcomes. Head and tail.
- When rolling a die, we will get 6 outcomes, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
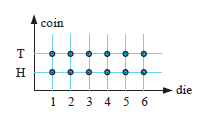
By converting the list,
{1H, 2H, 3H, 4H, 5H, 6H, 1T, 2T, 3T, 4T, 5T, 6T}
Problem 9 :
Rolling two dice
Solution :
By rolling each die, we will get 6 outcomes.
Outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
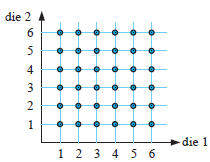
By converting it as list,
{(1, 1)(1, 2)
Problem 10 :
Rolling a die and spinning a spinner with sides A, B, C, D
Solution :
- When we roll a die, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
- When we roll a spinner, the possible outcomes are A, B, C and D.
Plotting the outcomes in horizontal and vertical axis.

By converting it as list,
{(1, A) (1, B) (1, C) (1, D) (2, A) (2, B) (2, C) (2, D) (3, A) (3, B) (3, C) (3, D) (4, A) (4, B) (4, C) (4, D) (5, A) (5, B) (5, C) (5, D) (6, A) (6, B) (6, C) (6, D) }
Problem 11 :
Twirling two square spinners :
One labelled A, B, C, D and the other 1, 2, 3, 4
Solution :
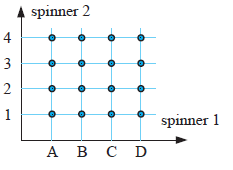
Outcomes of first spinner = A, B, C, D
Outcomes of second spinner = 1, 2, 3, 4
Sample space = {(A, 1) (A, 2) (A, 3) (A, 4) (B, 1) (B, 2) (B, 3) (B, 4) (C, 1) (C, 2) (C, 3) (C, 4) (D, 1) (D, 2) (D, 3) (D, 4)}
Illustrate on a tree diagram the sample space for
Problem 12 :
Tossing a 5 cent and 10 cent coin simultaneously.
Solution :
- A 5 cent coin will have two faces, head and tail
- A 10 cent coin will have two faces, head and tail
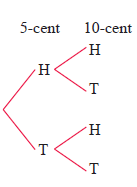
The possible outcomes are {HH, TT, HT, TH}
Problem 13 :
Tossing a coin and twirling an equilateral triangular spinner labelled A, B and C.
Solution :
- When we toss a coin, we get two outcomes head and tail
- When we are twirling a spinner, the possible outcomes are A, B, C and D.
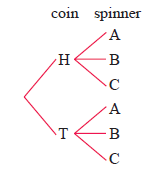
By converting it as list,
The possible outcomes are {(H, A) (H, B) (H, C) (T, A) (T, B) (T, C)
Problem 14 :
Draw a venn diagram to show a class of 20 students where 7 study History and Geography, 10 study History, 15 study Geography and 2 study neither subject.
Solution :
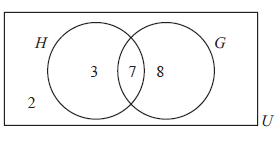
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling