PROPERTIES OF PARALLELOGRAM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Parallelogram
Definition of parallelogram :
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral which has opposite sides parallel.
Properties of parallelogram :
- Opposite sides are equal in length
- Opposite angles are equal in size.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
- Consecutive interior angles add upto 180.
Problem 1 :
Find each measure in parallelogram
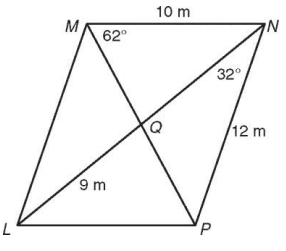
Find,
1) ML 2) LP 3) ∠LPM 4) ∠MLN 5) LN 6) QN
Solution :
Since it is parallelogram, the opposite sides are parallel and equal ML = PN and LP = MN
1) ML = 12 m
2) LP = 10 m
3) MN and LP are parallel, MP is a transversal.
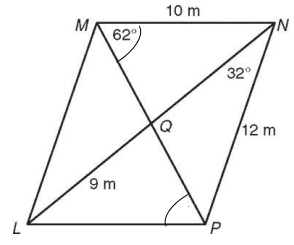
∠PMN = ∠LPM = 62° (Alternate interior angles)
4) ∠MLN
LM parallel to PN, then
∠MLN = ∠LNP = 32° (Alternate interior angles)
5) LN :
Since the diagonal will bisect each other, LP = NQ
LN = 2LP
LN = 2(9) ==> 18
6) QN = 9 m
Problem 2 :
CDEF is a parallelogram. Find each measure.
(i) CD (ii) EF (iii) ∠E (iv) ∠F
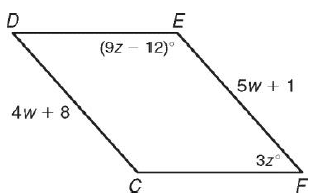
Solution :
In parallelogram opposite sides will be equal.
CD = EF
|
4w + 8 = 5w +1 4w - 5w = 1 - 8 -w = -7 w = 7 |
When w = 7 CD = 4w + 8 CD = 4(7) + 8 CD = 36 |
When w = 7 EF = 5w + 1 EF = 5(7) + 1 EF = 36 |
Sum of consecutive interior angles = 180.
9z - 12 + 3z = 180
12z - 12 = 180
12z = 192
z = 192/12
z = 16
|
(iii) ∠E = 9z - 12 ∠E = 9(16) - 12 ∠E = 144 - 12 ∠E = 132 |
(iv) ∠F = 3z ∠F = 3(16) ∠F = 48 |
Problem 3 :
Quadrilateral RSTU is a parallelogram. Find the values of x, y, a, and b.
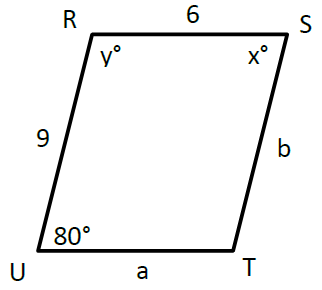
Solution :
x = 80°
x + y = 180 (Consecutive interior angles)
80 + y = 180
y = 180 - 80
y = 100
a = 6 and b = 9
Problem 4 :
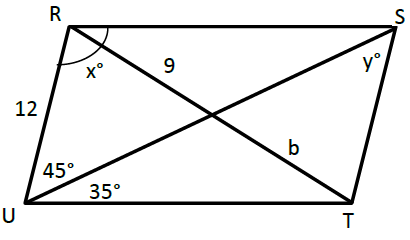
Solution :
In triangle RUS.
∠URS + ∠RSU + ∠SUR = 180
∠RSU = 35 (Alternate interior angles)
x + 35 + 45 = 180
x + 80 = 180
x = 180 - 80
x = 100
y = 45 (Alternate interior)
Diagonal will bisect each other. So, b = 9.
Problem 5 :
Find the missing measurements of parallelogram.
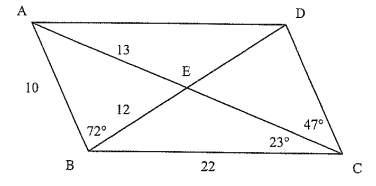
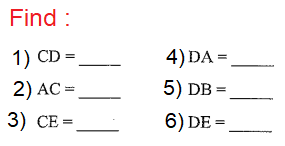
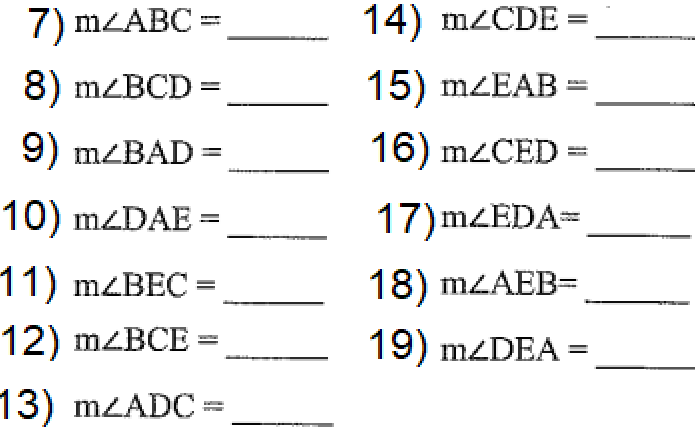
Solution :
1) CD = 10 (Opposite sides)
2) AC = 13 + 13 ==> 26
3) CE = 13
4) DA = 22 (Opposite sides)
5) DB = 12 + 12 ==> 24
6) DE = 12
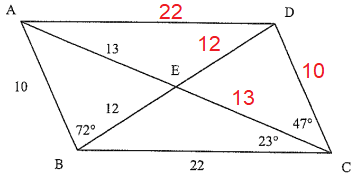
7) In triangle ABC,
∠EBC = x
∠EAB + ∠ABE + ∠EBC + ∠BCE = 180
47 + 72 + x + 23 = 180
142 + x = 180
x = 180 - 142
x = 38
∠ABC = 72 + 38 ==> 110
8) ∠BCD = 23 + 47 ==> 70
9) ∠BAD = 23 + 47 ==> 70
10) ∠DAE = 23
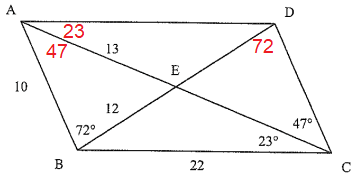
11) ∠BEC :
In triangle BEC,
38 + 23 + ∠BEC = 180
∠BEC = 180 - 61
∠BEC = 119
12) ∠BCE = 23
13) ∠ADC :
∠ABC = ∠ADC = 110 (opposite angles)
14) ∠CDE = 72 (Alternate angles)
15) ∠EAB = 47
16) ∠CED :
∠CED = 180 - (47 + 72)
∠CED = 180 - 119
∠CED = 61
17) ∠EDA = 38 (alternate interior angles)
18) ∠AEB = 61
19) ∠DEA = 119
Problem 8 :
In the figure given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. Find the values of x, y, z and p.
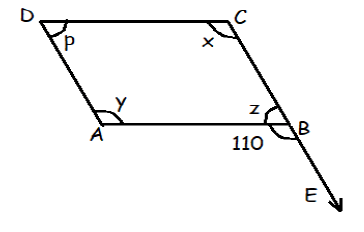
Solution :
110 + z = 180
z = 180 - 110
z = 70
In parallelogram sum of consecutive angles = 180
y + z = 180
y + 70 = 180
y = 110
Opposite angles are equal,
So, x = 110 and p = 70
Related Pages
- Find missing angles in parallelogram
- Find missing angles of parallelogram worksheet
- Length of diagonal of parallelogram
- Length of diagonal of parallelogram worksheet
- Properties of parallelogram worksheet
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling