PROBLEMS ON REFLECTION OVER HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL LINE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Reflection about horizontal and vertical lines :
For horizontal line of reflection, the vertical distance between a point and its reflection point will be the same from the line of reflection.
For vertical line of reflection, the horizontal distance between a point and its reflection point will be the same from the line of reflection.
Problem 1 :
Reflection across y = -1
R (-3, -5), N (-4, 0), V (-2, -1) E (0, -4)
Solution :
Plotting the points and creating the sides.
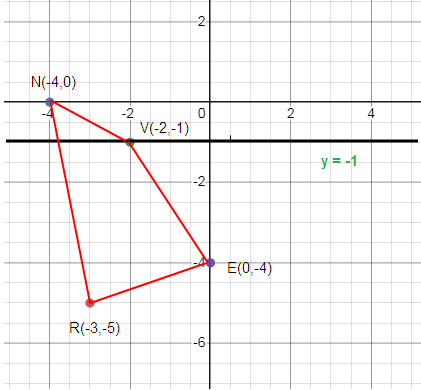
How to get R’?
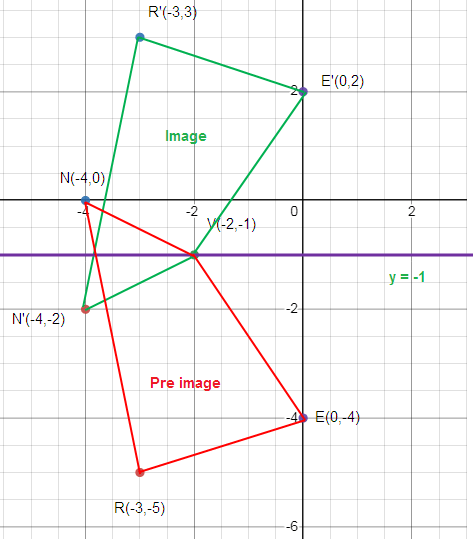
To reach R from y = -1, we move down 4 unit. So, to reach the reflection of R, that is R’ we have to move up 4 unit.
R (-3, -5) ==> R’ (-3, 3)
How to get N’?
To reach N from y = -1, we move up 1 unit. So, to reach the reflection of N, that is N’ we have to move down 1 unit.
N (-4, 0) ==> N’ (-4, -2)
How to get V’?
Distance between y = -1 and V is 0 unit. So, the same point is V’.
V and V’ are the same.
How to get E’?
To reach E from y = -1, we move down 3 unit. So, to reach the reflection of E, that is E’ we have to move up 3 unit.
E (0, -4) ==> E’ (0, 2)
Problem 2 :
Reflection across x = 3
F (2, 2), W (2, 5), K (3, 2)
Solution :
Plotting the points and creating the sides.
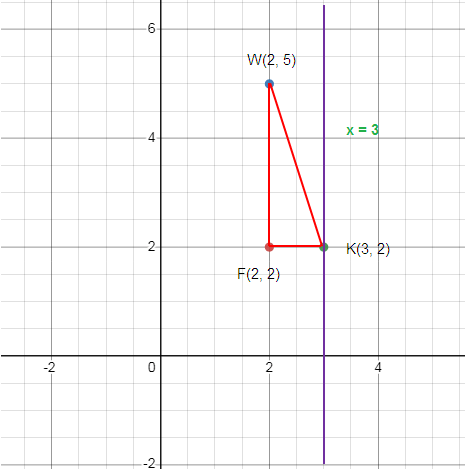
How to get F’?
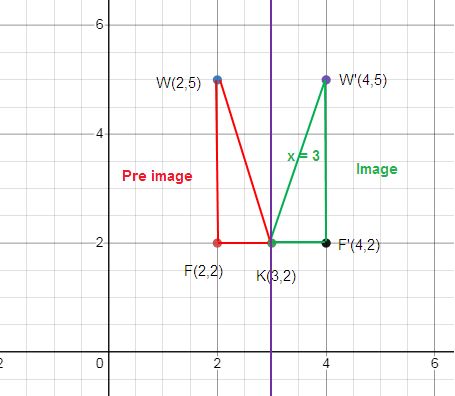
To reach F from x = 3, we move left 1 unit. So, to reach the reflection of F, that is F’ we have to move right 1 unit.
F (2, 2) ==> F’ (4, 2)
How to get K’?
Distance between x = 3 a nd K is 0 unit. So, the same point is K’.
K and K’ are the same.
How to get W’?
To reach W from x = 3, we move left 1 unit. So, to reach the reflection of W, that is W’ we have to move right 1 unit.
W (2, 5) ==> W’ (4, 5)
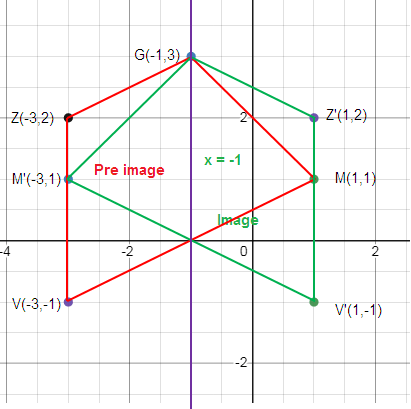
Problem 3 :
Reflection across x = -1
V (-3, -1), Z (-3, 2), G (-1, 3), M (1, 1)
Solution :
Plotting the points and creating the sides.
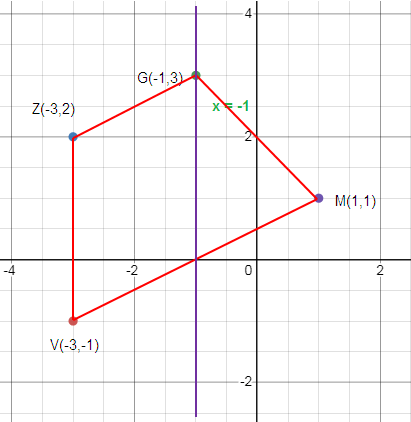
How to get V’?
To reach V from x = -1, we move left 2 unit. So, to reach the reflection of V, that is V’ we have to move right 2 unit.
V (-3, -1) ==> V’ (1, -1)
How to get Z’?
To reach Z from x = -1, we move left 2 unit. So, to reach the reflection of Z, that is Z’ we have to move right 2 unit.
Z (-3, 2) ==> Z’ (1, 2)
How to get G’?
Distance between x = -1 and G is 0 unit. So, the same point is G’.
G and G’ are the same.
How to get M’?
To reach M from x = -1, we move right 2 unit. So, to reach the reflection of M, that is M’ we have to move left 2 unit.
M (1, 1) ==> M’ (-3, 1)
Problem 4 :
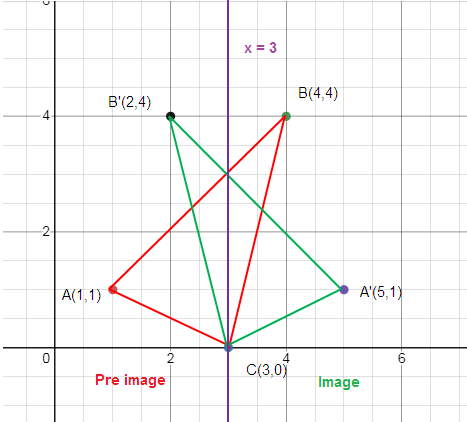
Reflection across x = 3
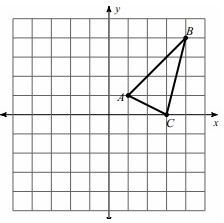
Solution :
By observing the triangle given above,
A (1, 1), B (4, 4) and C (3, 0)
How to get A’?
To reach A from x = 3, we move left 2 unit. So, to reach the reflection of A, that is A’ we have to move right 2 unit.
A (1, 1) ==> A’ (5, 1)
How to get B’?
To reach B from x = 3, we move right 1 unit. So, to reach the reflection of B, that is B’ we have to move left 1 unit.
B (4, 4) ==> B’ (2, 4)
How to get C’?
Distance between x = 3 and C is 0 unit. So, the same point is C’.
C and C’ are the same.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling