PROBLEMS ON MODULUS AND PRINCIPAL ARGUMENT OF COMPLEX NUMBER
The length of the line segment, that is OP, is called the modulus of the complex number. The angle from the positive axis to the line segment is called the argument of the complex number, z.
Example :
Find the modulus and argument of a complex number
1 + i
Solution :
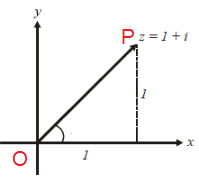
Let z = 1 + i
Finding Modulus :
Sum of squares of real part and imaginary part.
|
Modulus : OP = |z| = √12 + 12 OP = √2 |
Argument : θ = tan-1(y/x) θ = tan-1(1/1) θ = tan-1(1) θ = π/4 |
In the argant plane, angle lies in the
|
1st quadrant 2nd quadrant 3rd quadrant 4th quadrant |
θ = α θ = π - α θ = -π + α θ = - α |
Problem 1 :
The principal argument of 3/(-1 + i) is
|
|
|
Solution :
So, option (3) is correct.
Problem 2 :
The principal argument of (sin 40º + i cos 40º)5 is
(1) -110º (2) -70º (3) 70º (4) 110º
Solution :
Given, the principal argument of (sin 40º + i cos 40º)5
= (cos 50º + i sin 50º)5
= (cos 250º + i sin 250º)
250º lies in III quadrant.
To find the principal argument the rotation must be in a clockwise direction which coincides with 250º.
θ = -110º
So, option (1) is correct.
Problem 3 :
If (1 + i) (1 + 2i) (1 + 3i) … (1 + ni) = x + iy, then 2 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 10 … (1 + n2) is
(1)1 (2) i (3) x2 + y2 (4) 1 + n2
Solution :
(1 + i) (1 + 2i) (1 + 3i) … (1 + ni) = x + iy
Taking modulus on both sides.
|(1 + i) (1 + 2i) (1 + 3i) … (1 + ni)| = |(x2 + y2)|
So, option (3) is correct.
Problem 4 :
If ω ≠ 1 is a cubic root of unity (1 + ω)7 = A + Bω, then (A, B) equals
(1) (1, 0) (2) (-1, 1) (3) (0,1) (4) (1, 1)
Solution :
Given, (1 + ω)7 = A + Bω
1 + ω + ω2 = 0
1 + ω = -ω2
(1 + ω)7 = (-ω2)7
= -ω14
= -ω12 × ω2
= -(ω3)4 × ω2
= -ω2
= 1 + ω
= A + ωB
(A, B) = (1, 1)
So, option (4) is correct.
Problem 5 :
|
|
|
Solution :
So, option (4) is correct.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling