PRACTICE PROBLEMS ON TRIANGLES SIMILARITY
Problem 1 :
If △ABC ~ ARPQ, AB = 3 cm, BC = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm, RP = 6 cm and PQ = 10 cm, then find QR.
Solution:
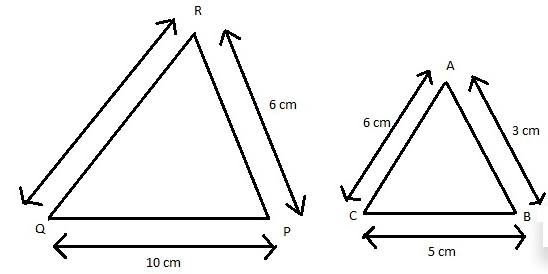
△ABC ≈ △RPQ
If two triangles are similar, then corresponding sides are proportional.
Problem 2 :
R and S are points on the sides DE and EF respectively of a ADEF such that ER = 5 cm, RD = 2.5 cm, SE = 1.5 cm and FS = 3.5 cm. Find whether RS || DF or not.
Solution:
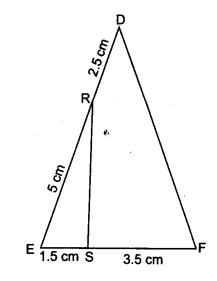
We have,
RE = 5 cm and RD = 2.5 cm
Similarity we have,
ES = 1.5 cm
SF = 3.5 cm
RS is not parallel to DF.
Problem 3 :
In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram and E divides BC in the ratio 1 : 3. DB and AE intersect at F. Show that DF = 4FB and AF = 4FE.
Solution:
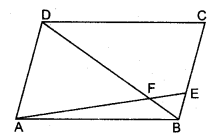
Given, ABCD is a parallelogram and BE : EC = 1 : 3
In △ADF and △EBF
∠ADF = ∠EBF (Alternate angles)
∠AFD = ∠EFB (Vertically opposite angle)
△ADF ~ △EBF (by alternate angle)
BC = BE + CE
= BE + 3BE
BC = 4BE
AD = BC
AD = 4BE
Put in (1), we get
Problem 4 :
In ADEW, AB || EW. If AD = 4 cm, DE = 12 cm and DW = 24 cm, then the value of DB.
Solution:
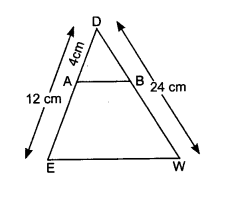
In △DEW, AB || EW
Problem 5 :
In figure, if ∠CAB = ∠CED, then prove that AB × DC = ED × BC.
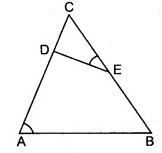
Solution:
Given,
∠CAB = ∠CED
In △CAB and △CED
∠1 = ∠2
∠C = ∠C
So,
△CAB ~ △CED
Hence, it is proved.
Problem 6 :
In △ABC, from A and B altitudes AD and BE are drawn. Prove that △ADC ~ △AEB and △ADB ~ △ADC?
Solution:
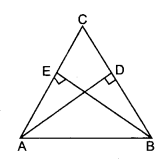
In △ADC and △BEC
∠D = ∠E
∠ACD = ∠BCE
So, △ADC ~ △BCE
△ADB is not similar to △AEB.
and △ADB is not similar to △ADC.
Problem 7 :
In △ABC, if ∠ADE = ∠B, then prove that △ADE ~ △ABC, if AD = 7.6 cm, AE = 7.2 cm, BE = 4.2 cm and BC = 8.4 cm, then find DE.
Solution:
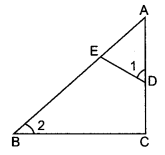
Given,
∠ADE = ∠B (ie) ∠1 = ∠2
In △ADE and △ABC
∠1 = ∠2
∠A = ∠ A
△ADE ~ △ABC
Problem 8 :
If in an equilateral triangle the length of the median is √3 cm, then find the length of the side of equilateral triangle.
Solution:
Let a be the side of equilateral triangle. Median is also the altitude in an equilateral triangle.
Side of triangle = 2 cm.
Problem 9 :
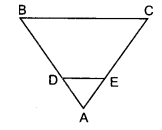
In the figure, D and E are points on AB and AC respectively such that DE||BC. If AD = 1/3 BD and AE = 4.5 cm, find AC.
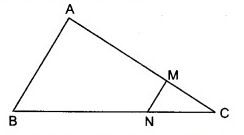
Solution:
Given,
DE||BC,
Problem 10 :
In the given figure, if LM || CB and LN || CD, prove that AM × AD = AB × AN.
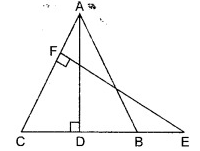
Solution:
In △BAC,
LM || BC
In △DAC,
LN || CD
From (1) and (2)
Hence, it is proved.
Problem 11 :
In the figure, PQR and SQR are two right triangles with common hypotenuse QR. If PR and SQ intersect at M such that PM = 3 cm, MR = 6 cm and SM = 4 cm, find the length of MQ.
Solution:
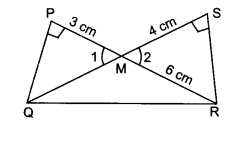
Consider the triangles MPQ and MSR.
∠P = ∠S
∠1 = ∠2
So, △MPQ ~ △MSR
Problem 12 :
In figure, DE || BC in AABC such that BC = 8 cm, AB = 6 cm and DA = 1.5 cm. Find DE.
Solution:
Given,, DE || BC
In △ADE and △ABC,
∠ADE = ∠ABC (corresponding angles)
∠A = ∠A
△ADE ~ △ABC
Problem 13 :
In figure, MN || AB, BC = 7.5 cm, AM = 4 cm and MC = 2 cm. Find the length BN.
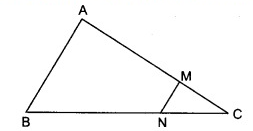
Solution:
In △ABC, MN || AB
△ABC ~ △MNC
Problem 14 :
In figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. E is a point on the side CB produced, such that FE ⊥ AC. If AD ⊥ CB. Prove that AB × EF = AD × EC.
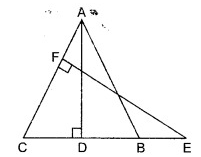
Solution:
In △ADB and △EFC,
∠D = ∠F and
∠B = ∠C (Angles opp to equal sides of a △ are equal)
△ABD ~ △ECF
AB × EF = AD × EC
Hence, it is proved.
Problem 15 :
The length of AB in the given figure:
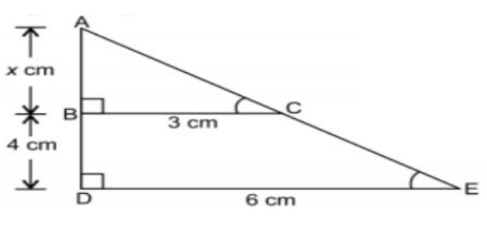
a) 8 cm b) 6 cm c) 4 cm d) 10 cm
Solution:
By using BPT,
△ABC ~ △ADE
BC || DE
So, option (c) is correct.
Problem 16 :
In the figure, DE || BC. If AD = x, BD = x - 2, AE = x + 2 and EC = x - 1, find the value of x.
Solution:
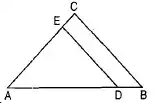
In △ABC, DE || BC
Problem 17 :
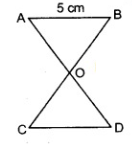
Solution:
In △AOB and △COD,
∠AOB = ∠COD (vertically opposite angles)
Therefore according to SAS similarity criterion, △AOB ~ △COD
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling