MAKING A SIGN CHART TO SOLVE INEQUALITY PROBLEMS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To solve inequality problems, we will follow the steps given below.
Step 1 :
Solve the inequality and find the value or values of x.
Step 2 :
Put the values in the number line and decompose into intervals.
Step 3 :
Select the values from the interval and apply in the factored form of the given inequality.
Step 4 :
Draw the sign chart in the given interval.
Step 4 :
The values from which interval is going to satisfy the given inequality can be considered as solution.
Step 5 :
In case we receive more than one intervals as solutions, use the Union to express the solution.
Make a sign chart to solve the inequalities. Give answers in interval solution.
Problem 1 :
x2 + 9x - 22 < 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = x2 + 9x - 22
Solving this quadratic function, we get
x2 + 9x - 22 = 0
Solving for x, we get
x2 + 11x - 2x - 22 = 0
x(x + 11) - 2(x + 11) = 0
(x - 2)(x + 11) = 0
x = 2 and x = -11

(-∞, -11), (-11, 2) and (2, ∞)
|
(-∞, -11) |
x = -12 |
f(x) = (x - 2)(x + 11) < 0 f(-12) = -14(-1) = 14 < 0 False |
|
(-11, 2) |
x = 0 |
f(x) = (x - 2)(x + 11) < 0 f(0) = -2(11) < 0 = -22 < 0 True |
|
(2, ∞) |
x = 3 |
f(x) = (x - 2)(x + 11) < 0 f(3) = 1(14) < 0 = 14 < 0 False |
Sign chart :
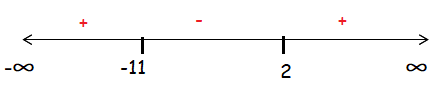
In the interval (-11, 2), the given function f(x) is true. Then the solution is (-11, 2).
Problem 2 :
x2 - 16 ≥ 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = x2 - 16
Solving this quadratic function, we get
x2 - 16 = 0
Solving for x, we get
(x + 4)(x - 4) = 0
x = -4 and x = 4

|
(-∞, -4] |
x = -5 |
f(x) = (x + 4)(x - 4) f(-5) = -1(-9) = 9 > 0 |
|
[-4, 4] |
x = 0 |
f(x) = (x + 4)(x - 4) f(0) = 4(-4) = -16 < 0 |
|
[4, ∞) |
x = 5 |
f(x) = (x + 4)(x - 4) f(5) = 9(1) = 9 > 0 |
Sign Chart :
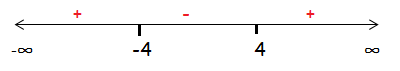
So, the solution is (-∞, -4] U [4, ∞).
Problem 3 :
x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) ≤ 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = x(x - 3)2 (x + 2)
Solving the function f(x), we get
x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) = 0
Equating each factor to 0, we get
x = 0, x = 3 and x = -2
Sign Chart :
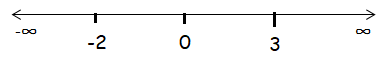
(-∞, -2], [-2, 0], [0, 3] and [3, ∞)
|
(-∞, -2] |
x = -3 |
f(x) = x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) ≤ 0 f(-3) = -3(36)(-1) ≤ 0 = 108 ≤ 0 False |
|
[-2, 0] |
x = -1 |
f(x) = x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) ≤ 0 f(-1) = -1(16)(1) ≤ 0 = -16 ≤ 0 True |
|
[0, 3] |
x = 1 |
f(x) = x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) ≤ 0 f(1) = 1(4)(3) ≤ 0 = 12 ≤ 0 False |
|
[3, ∞) |
x = 4 |
f(x) = x(x - 3)2 (x + 2) ≤ 0 f(4) = 4(1)(6) ≤ 0 = 24 ≤ 0 False |
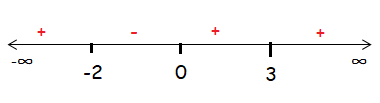
So, the solution is [-2, 0] and 3.
Problem 4 :
(x - 1) / (x + 4) ≤ 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 4)
Solving the function f(x), we get
(x - 1) / (x + 4) = 0
Equating the numerator and denominator to 0, we get
x = -4 and x = 1

(-∞, -4], [-4, 1] and [1, ∞)
|
(-∞, -4] |
x = -5 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 4) ≤ 0 f(-4) = -5/(-1) ≤ 0 = 5 ≤ 0 False |
|
[-4, 1] |
x = 0 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 4) ≤ 0 f(0) = -1/4 ≤ 0 True |
|
[1, ∞) |
x = 2 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 4) ≤ 0 f(2) = (2 - 1) / (2 + 4) ≤ 0 f(2) = 1/6 ≤ 0 False |
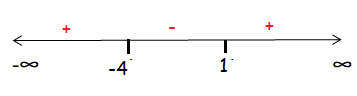
So, the solution is [-4, 1].
Problem 5 :
x2 / (x - 1) ≥ 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = x2 / (x - 1)
Solving the function f(x), we get
x2 / (x - 1) = 0
Equating the numerator and denominator to 0, we get
x = 0 and x = 1
Sign Chart :
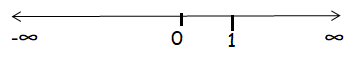
(-∞, 0] [0, 1] and [1, ∞)
|
(-∞, 0] |
x = -2 |
f(x) = x2 / (x - 1) ≥ 0 f(-2) = 4/(-3) ≥ 0 = False |
|
[0, 1] |
x = 0.5 |
f(x) = x2 / (x - 1) ≥ 0 f(0.5) = 0.25/(-0.5) ≥ 0 = False |
|
[1, ∞) |
x = 2 |
f(x) = x2 / (x - 1) ≥ 0 f(2) = 4/1 ≥ 0 = True |
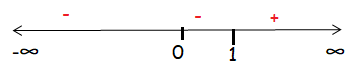
So, the required solution is 0 U [1, ∞).
Problem 6 :
(x2 -4x + 3) / (x2 + 4x - 21) > 0
Solution :
Let f(x) = (x2 -4x + 3) / (x2 + 4x - 21)
Solving the function f(x), we get
(x2 -4x + 3) / (x2 + 4x - 21)
Factoring the numerator,
x2 -4x + 3 = 0
(x - 1) (x - 3) = 0
x = 1 and x = 3
Factoring the denominator,
x2 + 4x - 21 = 0
(x - 3) (x + 7) = 0
x = 3 and x = -7
f(x) = (x - 1) (x - 3) / (x - 3) (x + 7) > 0
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 7) > 0
Sign chart :
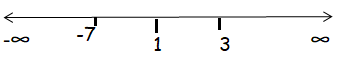
(- ∞, -7) (-7, 1) (1, 3) and (3, ∞).
|
(- ∞, -7) |
x = -8 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 7) > 0 f(-8) = -9/(-1) > 0 = 9 > 0 = True |
|
(-7, 1) |
x = 0 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 7) > 0 f(0) = -1/7 > 0 = False |
|
(1, 3) |
x = 2 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 7) > 0 f(2) = 1/9 > 0 = True |
|
(3, ∞) |
x = 4 |
f(x) = (x - 1) / (x + 7) > 0 f(4) = 3/11 > 0 = True |
So, the solution is (- ∞, -7), (1, 3) U (3, ∞).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling