INTERPRETING BAR GRAPHS
The representation of grouped data, in the form of vertical or horizontal rectangular bars, where
the lengths of the bars are = the measure of data
The bars drawn are of uniform width, and the variable quantity is represented on one of the axes. Also, the measure of the variable is depicted on the other axes.
The heights or the lengths of the bars denote the value of the variable, and these graphs are also used to compare certain quantities.
Types of bar graph :
(i) Horizontal graph
(ii) Vertical graph
Example 1 :
The bar graph shows the number of different items sold in an electrical goods store in a given month.
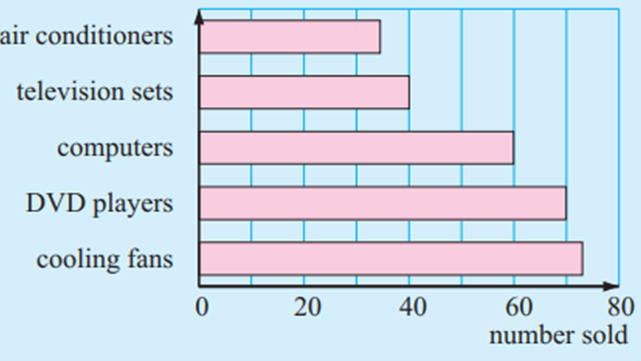
(a) How many DVD players were sold for the month ?
(b) How many more computers were sold than television sets ?
(c) What percentage of the items sold were cooling fans ?
Solution :
(a) By observing the bar graph, 70 DVD players were sold for the month.
(b) 60 computers were sold out.
(c) Number of air conditioners sold = 34
Number of television sets = 40
Number of computer sets = 60
DVD players = 70
Cooling fans = 73
Total = 34 + 40 + 60 + 70 + 73
= 277
Percentage of cooling fans = (73/277) x 100%
= 26.53%
= 27%
Example 2 :
(a) Estimate the median house price in 2008 in
(i) London
(ii) Liver pool
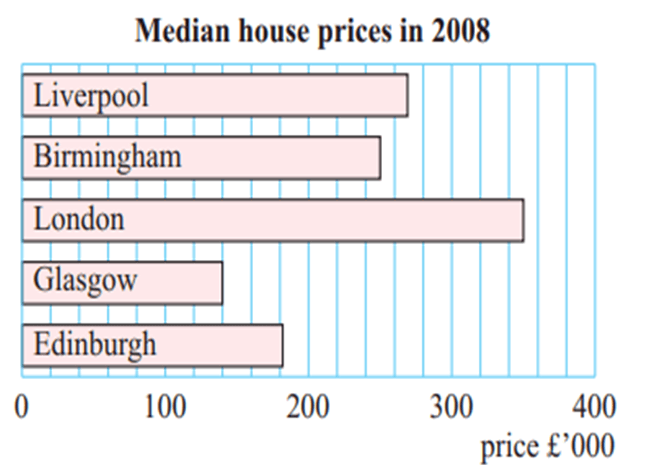
(b) How much bigger is the median house price in Edinburgh than Glasgow ?
(c) What percentage is the median Birmingham price of the median Liverpool price in the year 2008?
Solution :
(a) (i) length of bar of London = 353
Median price = 353 x 1000 ==> 353000
(ii) Liver pool = 278
Price = 278 x 1000 ==> 278000
(b) Price in Edinburg = 183 x1000 ==> 183000
Price in Glasgow = 140 x 1000 ==> 140000
Difference = 183000 - 140000
= 43000
(c) Price in Birmingham = 250000
Price in liver pool = 270000
Percentage = (250000/270000) x 100%
= 92.59%
Approximately 93%.
Example 3 :
The graph along side displays the result of a national phone in of children ages six to sixteen as to what they do at home between 3 pm to 6 pm
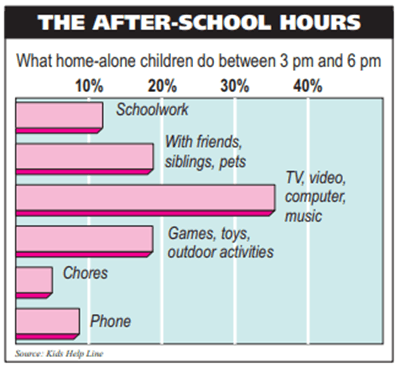
(a) Use the graph to determine the percentage of children who.
(i) Watch TV, videos, play with computers or listen to music.
(ii) Spend time with friends, siblings or pets.
(b) If 240 children were surveyed.
(i) How many do school work ?
(ii) How many spend more time on the phone rather than do chores ?
Solution :
(a) (i) 35% of children who watch TV, videos, play with computers or listen to music.
(ii) Which is closer to 20%, so 19% o children spend time with friends, siblings or pets.
(b) Number of children surveyed = 240
Number of children do school work = 12% of 240
= 0.12 (240)
= 28.8
So, 29 children do their school work.
(ii) Children spend time on phone = 9%
Number of children spend time on phone = 0.09(240)
= 21.6 approximately 22
Children spend time Chores = 5%
Number of children spend time on chores = 0.05(240)
= 12
= 22 - 12
= 10 children
Example 4 :
The bar graphs shows the crude oil reserves for the top five oil producing countries in the world.
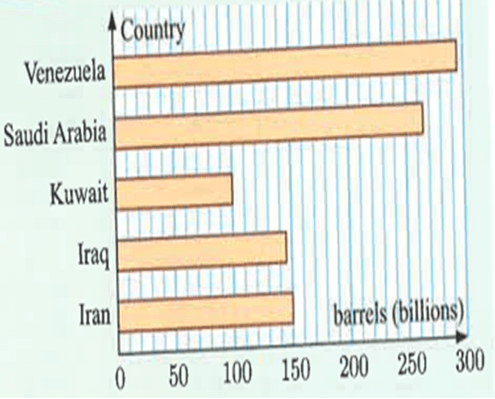
(a) How many billion barrels of crude oil do these countries have in total ?
(b) How many more barrels can Saudi Arabia produce than Iraq?
(c) What percentage of the crude oil is held by Iran ?
Solution :
Iran = 150, Iraq = 145, Kuwait = 100, Saudi Arabia = 255, Venezuela = 295
Total = 150 + 145 + 100 + 265 + 295
= 955
So, 955 barrels are in total.
(b) Number of barrels produced by Iraq = 145
Number of barrels produced by Saudi Arabia = 255
Difference = 255 - 145 ==> 110
So, Saudi Arabia has produced 110 more barrels than Iraq.
(c) Quantity of Crude oil produced in Iran = 150
Percentage = (150/955) x 100%
= 15.70%
So, 15.7% of crude oil produced by Iran.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling