HOW TO FIND CHARACTERSTICS OF GRAPHS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Domain :
How the graph is spread on the x-axis is domain. In other words, for the set of x values for which it is spreading horizontally, that is known as domain.
Range :
How the graph is spread on the y-axis is range. In other words, for the set of y-values for which it is spreading vertically, that is known as range.
Maximum or minimum :
The point where the graph reaches its maximum height is maximum. When the curve changes its direction from increasing to decreasing, there will be a maximum point.
The point where the graph reaches its minimum height is minimum. When the curve changes its direction from decreasing to increasing, there will be a minimum point.
x and y intercepts :
The curve where it cuts the x-axis is known as x-intercept, the curve where it cuts the y-axis is known as y-intercept.
How to check if it is discreate or continuous ?
Discrete functions have scatter plots as graphs and continuous functions have lines or curves as graphs.
Problem 1 :
Use the graphs to state the various features.
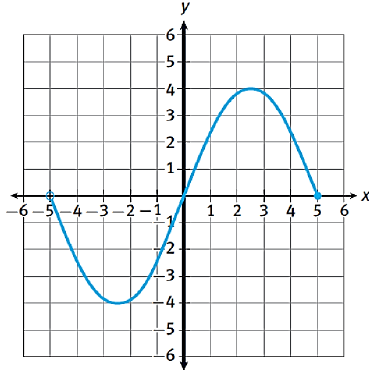
|
i) Domain ii) Range iii) Maximum iv) Minimum |
v) Discrete or Continuous? vi) y – intercept: vii) x – intercept: viii) 7𝑓(5)= |
Solution :
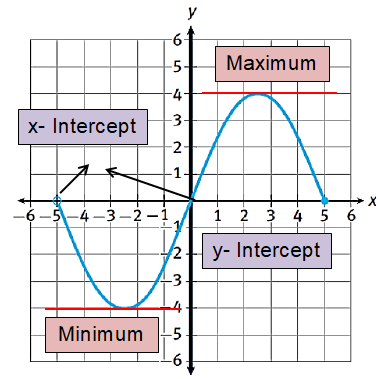
|
i) Domain: (-5, 5] ii) Range : [-4, 4] iii) Maximum: y = 4 iv) Minimum: y = -4 |
v) Discrete or Continuous? Continuous vi) y – intercept: y = 0 vii) x – intercept: x = 0 and x = 5 viii) 7 𝑓(5) = 0 |
Problem 2 :
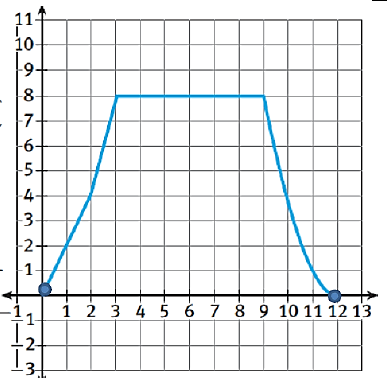
|
i) Domain: ii) Range: iii) Maximum: iv) Minimum: |
v) Interval of Increase: vi) Interval of Decrease: vii) 𝑓(2) + 𝑓(9) = |
Solution :
i) Domain : [0, 12]
ii) Range: [0, 8]
iii) Maximum: y = 8
iv) Minimum: y = 0
v) Interval of Increase: (0, 3)
vi) Interval of Decrease: (9, 12)
vii) 𝑓(2) = 4 and 𝑓(9) = 8
f(2) + f(9) = 4 + 8 ==> 12
Problem 3 :
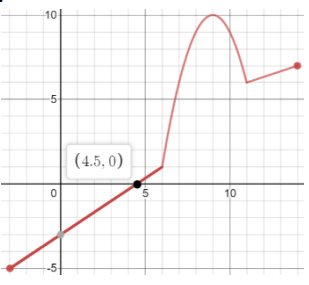
|
i) Domain ii) Increasing iii) Range iv) Decreasing v) x-intercept (s) |
vi) Positive vii) y-intercept viii) Negative ix) Maximum x) Minimum xi) End behaviour |
Solution :
|
Domain Increasing Range Decreasing x-intercept(s) Positive y-intercept Negative Maximum Minimum |
[-3, 14] (-3, 9) ꓴ (11, 14) [-5, 10] (9,14) (4.5,0) (4.5,14] (0,-3) [-3,4.5) (9,10) (-3,-5) |
End Behavior: 𝑎𝑠 x → −3, y → −5; 𝑎𝑠 x → 14, y → 10
Problem 4 :
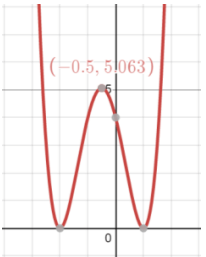
|
i) Domain ii) Range iii) x-intercept(s) iv) y-intercept v) Maximum |
vi) Increasing vii) Decreasing viii) Positive ix) Negative x) Minimum xi) End behaviors |
Solution :
|
Domain Increasing Range Decreasing x-intercept(s) Positive y-intercept Negative Maximum Minimum End Behavior |
(-∞, ∞) (-2,-0.5) ꓴ (1, ∞) (0, ∞) (-∞,-2) ꓴ (-0.5,1) (-2,0) & (1,0) (-∞,-2) ꓴ (-2,1) ꓴ(1, ∞) (0,4) none (-0.5,5.063) (-2,0) & (1,0) x → −∞, y → +∞; 𝑎𝑠 x → +∞, y → +∞ |
Problem 5 :
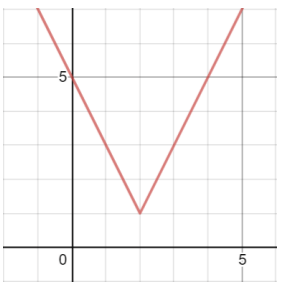
|
i) Domain ii) Increasing iii) Range iv) Decreasing v) x-intercept(s) |
vi) Positive vii) y-intercept viii) Maximum ix) Minimum x) End behavior |
Solution :
|
i) Domain ii) Increasing iii) Range iv) Decreasing v) x-intercept(s) vi) Positive vii) y-intercept viii) Maximum ix) Minimum x) End behavior |
(-∞, ∞) (2, ∞) (1, ∞) (-∞,2) none (-∞, ∞) (0,5) none (2,1) x → −∞, y → +∞; 𝑎𝑠 x → +∞, y → +∞ |
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling