FIND THE VALUE OF TRIGONOMETERIC FUNCTIONS IN THE GIVEN QUADRANT
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1:
Find sin θ if cos θ = 2/3, 0
< θ < π/2
Solution:
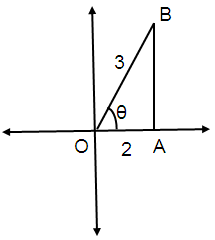
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
Cos θ = 2/3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
AB² = OB² - OA²
AB² = 3² - 2²
AB = √9 - 4
AB = √5
θ is in I quadrant.
All trigonometric values are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = √5/3
Problem 2 :
Find cos θ, if sin θ = 2/5, π/2 < θ < π
Solution :
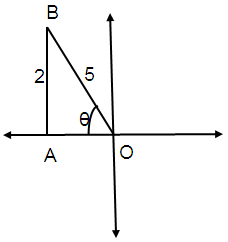
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = 2/5
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OA² = OB² - AB²
OA² = 5² - 2²
OA = √25 - 4
OA = √21
θ is in II quadrant.
In 2nd quadrant only sin and cosec are positive.
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = -√21/5
Problem 3 :
Find cos θ if sin θ = -3/5, 3π/2 < θ < 2π
Solution :
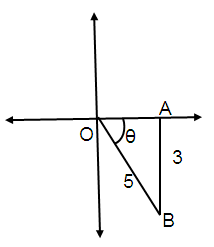
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = -3/5
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OA² = OB² - AB²
OA² = 5² - (-3)²
OA = √25 - 9
OA = √16
OA = 4
θ is in IV quadrant.
In 4th quadrant only cos and sec are positive.
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = 4/5
Problem 4 :
Find sin θ if cos θ = -5/13,
π < θ < 3π/2
Solution :
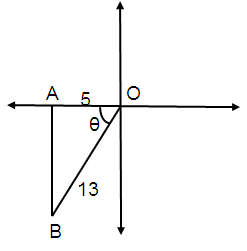
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
Cos θ = -5/13
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
AB² = OB² - OA²
AB² = 13² - (-5)²
AB = √169 - 25
AB = √144
AB = 12
θ is in III quadrant.
In 3rd quadrant only tan and cot are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = -12/13
Problem 5 :
if sin x = 1/3 and π/2
< x < π, find tan x in radical (surd) form.
Solution :
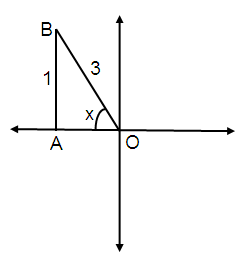
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = 1/3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OA² = OB² - AB²
OA² = 3² - 1²
OA = √9 - 1
OA = √8
OA = 2√2
x is in II quadrant.
In 2nd quadrant only sin and cosec are positive.
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = -1/2√2
Problem 6 :
if cos x = 1/5 and 3π/2 < x < 2π, find tan x in radical (surd) form.
Solution :
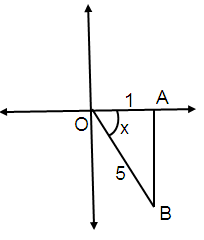
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = 1/5
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
AB² = OB² - OA²
AB² = 5² - 1²
AB = √25 - 1
AB = √24
AB = 2√6
x is in IV quadrant.
In 4th quadrant only cos and sec are positive.
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = -2√6 / 1
tan x = -2√6
Problem 7 :
if sin x = -1/√3 and π < x < 3π/2, find tan x in radical (surd) form.
Solution :
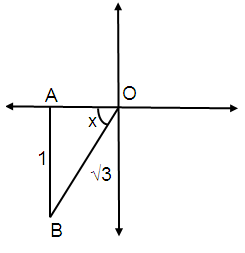
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = -1/√3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OA² = OB² - AB²
OA² = (√3)² - 1²
OA = 3 - 1
OA = √2
x is in III quadrant.
In 3rd quadrant only tan and cot are positive.
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = 1/√2
Problem 8 :
if cos x = -3/4 and π/2 < x < π, find tan x in radical (surd) form.
Solution :
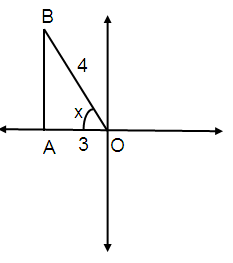
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = -3/4
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
AB² = OB² - OA²
AB² = 4² - 3²
AB = √16 - 9
AB = √7
x is in II quadrant.
In 2nd quadrant only sin and cosec are positive.
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = -√7/3
Problem 9 :
Find sin x and cos x given that:
tan x = 2/3 and 0 < x < π/2
Solution :
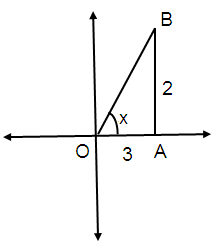
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = 2/3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OB² = 2² + 3²
OB = √4 + 9
OB = √13
x is in I quadrant.
All trigonometric values are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
Sin θ = 2/√13
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = 3/√13
Problem 10 :
tan x = -4/3 and π/2 < x < π
Solution :
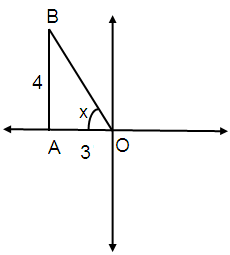
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = -4/3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OB² = 4² + 3²
OB = √16 + 9
OB = √25
OB = 5
x is in II quadrant.
In 2nd quadrant only sin and cosec are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
Sin θ = 4/5
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = -3/5
Problem 11 :
tan x = √5/3 and π < x < 3π/2
Solution :
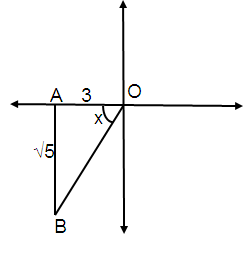
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = √5/3
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OB² = (√5)² + 3²
OB = √5 + 9
OB = √14
x is in III quadrant.
In 3rd quadrant only tan and cot are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = -√5/√14
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = -3/√14
Problem 12 :
tan x = -12/5 and 3π/2 < x < 2π
Solution :
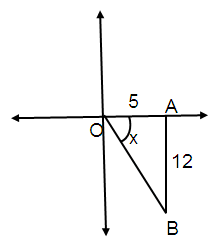
tan x = Opposite / Adjacent
tan x = -12/5
By using Pythagorean Theorem,
OB² = AB² + OA²
OB² = 12² + 5²
OB = 144 + 25
OB = √169
OB = 13
x is in IV quadrant.
In 4th quadrant only cos and sec are positive.
sin θ = Opposite / Hypotenuse
sin θ = -12/13
cos θ = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
cos θ = 5/13
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling