FIND DOMAIN OF RATIONAL FUNCTION WITH RADICAL AS INTERVAL NOTATION
State the domain in interval notation.
Problem 1 :
Solution:
Equate the denominator to zero.
x - 3 = 0
x = 3
If x = 3, then the denominator becomes zero and the value of 'y' becomes undefined.
So, 'y' is defined for all real values of 'x' except x = 3.
Therefore, the domain is
R - {3}
In interval notation,
(-∞, 3)∪(3, ∞)
Problem 2 :
Solution:
Equate the denominator to zero.
x2 - 25
x2 - 52 = 0
Using algebraic identity a2 - b2 = (a + b)(a - b)
(x + 5)(x - 5) = 0
x + 5 = 0 or x - 5 = 0
x = -5 or x = 5
The domain is all real values except -5 and 5.
In interval notation,
(-∞, -5)∪(-5, 5)∪(5, +∞)
Problem 3 :
Solution:
Equate the denominator to zero.
x2 + 4x - 21 = 0
x2 + 7x - 3x - 21 = 0
x(x + 7) - 3(x + 7) = 0
(x + 7) (x - 3) = 0
x = -7 or x = 3
The domain is all real values except -7 and 3.
In interval notation,
(-∞, -7)∪(-7, 3)∪(3, +∞)
Problem 4 :
Solution:
Equate the denominator to zero.
3x2 + 9x = 0
3x(x + 3) = 0
3x = 0 or x + 3 = 0
x = 0 or x = -3
The domain is all real values except 0 and -3.
In interval notation,
(-∞, -3)∪(-3, 0)∪(0, +∞)
Problem 5 :
Solution:
2x - 8 = 0
x = 4
√(x2- 36) ≥ 0
x2- 36 ≥ 0
x2 ≥ 36
x ≥ ±6

Decomposing into intervals.
(-∞, -6), (-6, 4) (4, 6) and (6, ∞)
|
(-∞, -6) x = -7 ∈ (-∞, -6) √((-7)2- 36) ≥ 0 √(49-36) ≥ 0 √13 ≥ 0 (true) |
(-6, 4) x = 0 ∈ (-6, 4) √(02- 36) ≥ 0 √-36 ≥ 0 (False) |
|
(4, 6) x = 5 ∈ (4, 6) √(52- 36) ≥ 0 √-9 ≥ 0 (False) |
(6, ∞) x = 7 ∈ (6, ∞) √(72- 36) ≥ 0 √13 ≥ 0 (True) |
Domain is (-∞, -6) U (6, ∞).
Problem 6 :
Solution:
3x - 24 = 0
x = 8
√(x2- 25) ≥ 0
x2- 25 ≥ 0
x2 ≥ 25
x ≥ ±5

Decomposing into intervals.
(-∞, -5), (-5, 5) (5, 8) and (8, ∞)
|
(-∞, -5) x = -6 ∈ (-∞, -5) √((-6)2- 25) ≥ 0 √9 ≥ 0 (true) |
(-5, 5) x = 0 ∈ (-5, 5) √(02- 25) ≥ 0 √-25 ≥ 0 (False) |
|
(5, 8) x = 6 ∈ (5, 8) √(62- 36) ≥ 0 0 ≥ 0 (True) |
(8, ∞) x = 9 ∈ (8, ∞) √(92- 36) ≥ 0 (True) |
So, the domain is (-∞, -5),(5, 8) and (8, ∞).
Problem 7 :
Solution:
x2+7x+10 = 0
(x + 5)(x + 2) = 0
x = -5 and x = -2
√(9 - x2) ≥ 0
9 - x2 ≥ 0
-x2 ≥ -9
x2 ≤ 9
x ≥ ±3
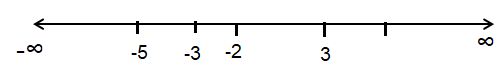
Decomposing into intervals.
(-∞, -5), (-5, -3) (-3, -2), (-2, 3) and (3, ∞)
|
(-∞, -5) x = -6 ∈ (-∞, -5) √(9 - (-6)2) ≥ 0 √-7 ≥ 0 (False) |
(-5, -3) x = -4 ∈ (-5, -3) √(9 -(-4)2) ≥ 0 √-7 ≥ 0 (False) |
|
(-3, -2) x = -2.5 ∈ (-3, -2) √(9 - (-2.5)2) ≥ 0 (True) |
(-2, 3) x = 0 ∈ (-2, 3) √(9 - 02) ≥ 0 (True) (3, ∞) x = 4 ∈ (3, ∞) √(9 - 42) ≥ 0 (False) |
So, the domain is (-3, -2) and (-2, 3).
Problem 8 :
Solution :
√(5x3 - 9) ≥ 0
For all negative values of x, we will get negative values. So, only positive values are applicable.
(5x3 - 9) = 0
5x3 = 9
x3 = 9/5
x = cube root (1.8) ==> 1.216
Equating the denominator to 0, we get
x3 +13x2 + 42x = 0
x(x2 +13x + 42) = 0
x(x + 6)(x + 7) = 0
x = 0, x = -6 and x = -7
Here all these values should be excluded from domain. So, the required domain is x ≥ 1.216
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling