EXTERIOR ANGLE THEOREM OF TRIANGLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
An interior angle of a triangle is formed by two sides of the triangle. An exterior angle is formed by one side of the triangle and the extension of an adjacent side.
Each exterior angle has two remote interior angles. A remote interior angle is an interior angle that is not adjacent to the exterior angle.
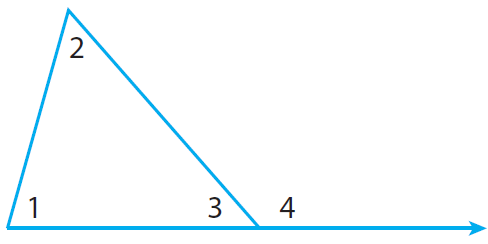
Extend the base of the triangle and label the exterior angle as ∠4.
The Triangle Sum Theorem states :
m∠1 + m∠2 + m∠3 = 180 -----(1)
So, m∠3 + m∠4 = 180 -----(2)
(2) = (1)
m∠1 + m∠2 + m∠3 = m∠3 + m∠4
m∠1 + m∠2 = m∠4
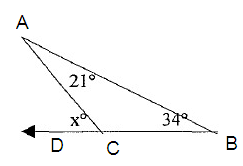
Problem 1 :
Solve for x.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write the Exterior Angle Theorem as it applies to this triangle.
m ∠ A + m ∠ B = m ∠ ACD
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
21º + 34º = xº
Step 3 :
55º = xº
So, the value of x is 55º.
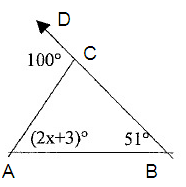
Problem 2 :
Solve for x and find m ∠A.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write the Exterior Angle Theorem as it applies to this triangle.
m ∠A + m ∠B = m ∠C
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
(2x + 3)º + 51º = 100º
Step 3 :
Solve the equation for x.
(2x + 3)º + 51º = 100º
2x + 3 + 51 = 100
2x + 54 = 100
Subtract 54 from both sides.
2x + 54 – 54 = 100 – 54
2x = 46
Divide both sides by 2.
2x/2 = 46/2
x = 23
Step 4 :
Use the value of x to find m ∠A.
m ∠A = 2x + 3
= 2(23) + 2
= 46 + 2
m ∠ A= 48
So, the value of m ∠A is 48º.
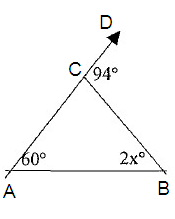
Problem 3 :
Solve for x and find m ∠B.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write the Exterior Angle Theorem as it applies to this triangle.
m ∠A + m ∠B = m ∠C
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
60º + 2xº = 94º
Subtract 60º from both sides.
60º - 60º + 2xº = 94º - 60º
2xº = 34
Divide both sides by 2.
2xº/2 = 34/2
xº = 17
Step 3 :
Use the value of x to find m ∠ B.
m ∠ B = 2xº
= 2(17)
= 34
So, the value of m ∠B is 34º.
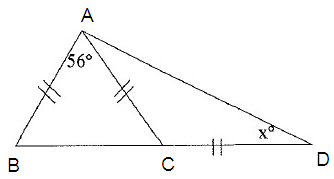
Problem 4 :
Solve for x.
Solution :
Step 1 :
m ∠DCA = m ∠CAB + m ∠ABC
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
6x - 7 = 2x + 103 - x
6x - 7 = x + 103
6x - x = 103 + 7
5x = 110
x = 110/5
x = 22
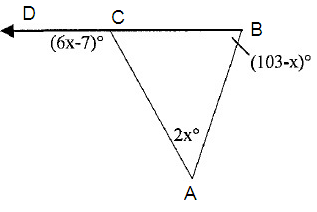
Problem 5 :
Solve for x.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write the Exterior Angle Theorem as it applies to this triangle.
In a triangle ∠ABC
m ∠A + m ∠B + m ∠C = 180º
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
50º + 62º + m ∠C = 180º
112 + m ∠C = 180º
Subtract 112 from both sides.
m ∠C = 180 - 112
x = 68
Step 3 :
In a triangle ∠DEF
m ∠D + m ∠E + m ∠F = 180º
Step 4 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
53º + m ∠E + 80º = 180º
133 + m ∠E = 180º
m ∠E = 180 - 133
m ∠E = 47
Step 5 :
∠EOC = 180 – (∠ABC + ∠DEF)
= 180 - 115
= 65
So, the value of x is 65.
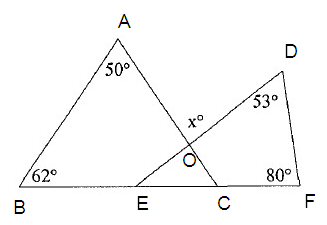
Problem 6 :
Solve for x, find m ∠ A.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Write the Exterior Angle Theorem as it applies to this triangle.
m ∠A + m ∠B = m ∠C
Step 2 :
Substitute the given angle measures.
xº + 90º = 122º
Step 3 :
x + 90 = 122
Subtract 90 from both sides.
x + 90 – 90 = 122 - 90
x = 32
Step 4 :
Use the value of x to find m ∠A.
m ∠A = xº
= 32
So, the value of m ∠ A is 32.
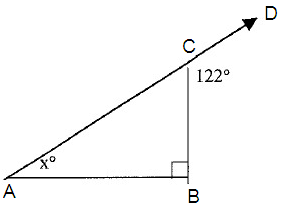
Problem 7 :
Solve for x.
Solution :
In triangle ABC,
∠ABC = ∠ACB
∠BAC = 56º
∠CDA = xº
∠ABC + ∠ACB + ∠BAC = 180
2∠ABC + 56 = 180
2∠ABC = 180 - 56
2∠ABC = 124
∠ABC = 124/2
∠ABC = 62
∠ACD = 56 + 62 ==> 118
∠CAD = ∠CDA = x
x + x + 118 = 180
2x + 118 = 180
2x = 62
x = 31
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling