DOMAIN OF COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To find domain of composition of function, we have to consider the following.
i) Find composition of functions.
ii) If the composition function is polynomial function, that will be defined for all real values. So, domain will be (-∞, ∞).
iii) If the composition function is square root function, then after applying the value of x, we should not receive negative values inside the square root. On this condition, we have to fix the domain.
iv) If we have rational function, the denominator should never become 0. The values which are making the denominators 0, we have to exclude those values from domain.
For each of the following problems :
(a) Find f ∘ g and its domain.
(b) Find g ∘ f and its domain.
Problem 1 :
f(x) = x2 + 3x; g(x) = 2x - 7
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
= f[2x - 7]
= (2x - 7)2 + 3(2x - 7)
= (2x)2 + 72 - 2(2x)(7) + 6x - 21
= 4x2 + 49 - 28x + 6x - 21
(f ∘ g)(x) = 4x2 - 22x + 28
Domain is all real values of x.
So, domain of f ∘ g is (-∞, ∞).
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
= g[x2 + 3x]
= 2(x2 + 3x) - 7
(g ∘ f)(x) = 2x2 + 6x - 7
Domain is all real values of x.
So, domain of g ∘ f is (-∞, ∞).
Problem 2 :
f(x) = 6x + 2; g(x) = 7 - x2
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
= f[7 - x2]
= 6(7 - x2) + 2
= 42 - 6x2 + 2
(f ∘ g)(x) = 44 - 6x2
So, domain of f ∘ g is (-∞, ∞).
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
= g[6x + 2]
= 7 - (6x + 2)2
= 7 - [(6x)2 + 22 + 2(6x)(2)]
= 7 - [36x2 + 4 + 24x]
= 7 - 36x2 - 4 - 24x
(g ∘ f)(x) = -36x2 - 24x + 3
So, domain of g ∘ f is (-∞, ∞).
Problem 3 :
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
So, domain of f ∘ g is all real numbers expect 4.
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
= g(x2)
√(x2 - 4) ≥ 0
(x2 - 4) ≥ 0
(x + 2)(x - 2) ≥ 0
By drawing number line, we will get the solution more clearly.
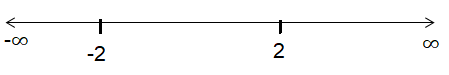
x = -3 ∈ (-∞, -2)
Appling the above value in (x + 2) (x - 2) ≥ 0, we get
(-3+2)(-3-2) ≥ 0
True
x = 0 ∈ (-2, 2)
Appling the above value in (x + 2) (x - 2) ≥ 0, we get
(0+2)(0-2) ≥ 0
False
x = 4 ∈ (2, ∞)
Appling the above value in (x + 2) (x - 2) ≥ 0, we get
(4+2)(4-2) ≥ 0
True
So, domain of g ∘ f is (-∞, -2) ∪ (2, ∞).
Problem 4 :
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
= f(x)2
Domain is all real values. Because no values will make the denominator as zero. Then the entire function will not become undefined for any values.
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
So, domain of g ∘ f is all real numbers except -5.
Problem 5 :
f(x) = √(x + 7); g(x) = -5 - x
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
= f[-5 - x]
= √(-5 - x + 7)
(f ∘ g)(x) = √(2 - x)
So, domain of f ∘ g is (-∞, 2]
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
= g[√(x + 7)]
(g ∘ f)(x) = -5 - √(x + 7)
So, domain of g ∘ f is [-7, ∞).
Problem 6 :
f(x) = √(3 - x); g(x) = 9 - 2x
Solution :
(a) To find f ∘ g and its domain :
f ∘ g = f[g(x)]
= f[9 - 2x]
= √(3 - (9 - 2x))
= √(3 - 9 + 2x)
(f ∘ g)(x) = √(2x - 6)
So, domain of f ∘ g is [3, ∞).
(b) To find g ∘ f and its domain :
g ∘ f = g[f(x)]
= g[√(3 - x)]
= 9 - 2(√(3 - x))
(g ∘ f)(x) = 9 - 2√3 + 2x
So, domain of g ∘ f is (-∞, ∞).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling