Converting Between Standard Vertex and Factored Form
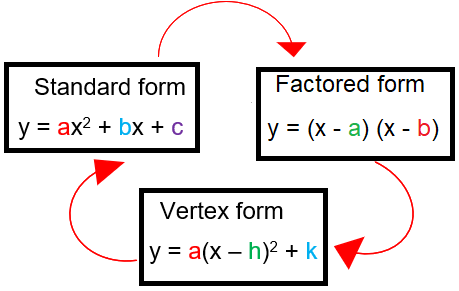
Given one of the forms of a quadratic function, convert to the other two forms.
Problem 1 :
y = x2 − 6x − 7
(i) Vertex form
(ii) Factored form
Solution :
(i) Converting into vertex form :
y = x2 − 6x − 7
Coefficient of x2 is 1. So, don't have to factories anything.
Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2.
y = x2 − 2⋅x⋅3 + 32 - 32 - 7
y = (x - 3)2 - 32 - 7
y = (x - 3)2 - 9 - 7
y = (x - 3)2 - 16
y = (x - h)2 + k
Vertex (h, k) is (3, -16).
(i) Converting into factored form :
y = x2 − 6x − 7
Decomposing -7, we get 1 (-7).
1(-7) = -7, 1 + (-7) = -6
y = x2 + 1x - 7x − 7
y = x(x + 1) - 7(x + 1)
y = (x + 1) (x - 7)
So, -1 and 7 are x-intercepts.
Problem 2 :
y = 3(x − 1)2 − 3
(i) Standard form
(ii) Factored form
Solution :
(i) Converting into standard form :
y = 3(x − 1)2 − 3
Here (x-1)2 looks like (a - b)2.
(a - b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2
(x − 1)2 = x2 - 2x(1) + 12
(x − 1)2 = x2 - 2x - 3
y = 3(x2 - 2x + 1) - 3
y = 3x2 - 6x + 3 - 3
y = 3x2 - 6x
(ii) Converting into factored form :
y = 3x2 - 6x
Factor 3x, we get
= 3x (x - 2)
So, 0 and 2 are x-intercepts.
Problem 3 :
y = 2(x − 3)(x + 5)
(i) Vertex form:
(ii) Standard form:
Solution :
(i) Converting into vertex form :
y = 2(x − 3)(x + 5)
y = 2(x2 + 5x - 3x - 15)
y = 2(x2 + 2x - 15)
y = 2(x2 + 2⋅x⋅1 + 12 - 12 - 15)
y = 2[(x + 1)2 - 12 - 15]
y = 2[(x + 1)2 - 16]
y = 2(x + 1)2 - 32
So, vertex is (-1, -32).
(ii) Converting into standard form :
y = 2(x − 3)(x + 5)
y = 2(x − 3)(x + 5)
y = 2(x2 + 5x - 3x - 15)
y = 2(x2 + 2x - 15)
Distributing 2, we get
y = 2x2 + 4x - 30
Problem 4 :
y = 2x2 + 8x + 10
(i) Vertex form:
(ii) Factored form
Solution :
(i) Converting into vertex form :
y = 2x2 + 8x - 10
y = 2(x2 + 4x - 5)
y = 2(x2 + 2⋅x⋅2 + 22 - 22 - 5)
y = 2[(x+2)2 - 4 - 5)]
y = 2[(x+2)2 - 9]
y = 2(x+2)2 - 18
So, the vertex is (-2, -18).
(ii) Converting into factored form :
y = 2x2 + 8x - 10
y = 2(x2 + 4x - 5)
y = 2(x - 52 + 4x - 5)
Problem 5 :
𝑦 = 2(𝑥 + 1)2 − 8
(i) Standard form
(ii) Factored form
Solution :
(i) Converting into standard form :
𝑦 = 2(𝑥 + 1)2 − 8
Using the algebraic identity (a + b)2, we can find the expansion of (x + 1)2
(x + 1)2 = x2 + 2⋅x⋅1 + 12
(x + 1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1
y = 2(x2 + 2x + 1) − 8
y = 2x2 + 4x + 2 − 8
y = 2x2 + 4x − 6
(ii) Converting into factored form :
y = 2x2 + 4x − 6
Factoring 2, we get
y = 2(x2 + 2x − 3)
y = 2(x - 1) (x + 3)
Problem 6 :
y = −4(x + 1)(2x − 5)
(i) Vertex form:
(ii) Standard form:
Solution :
(i) Converting into vertex form :
y = −4(x + 1)(2x − 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 5x + 2x - 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 3x - 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 3x - 5)
So, the vertex is (3/4, 49/2).
(ii) Converting into standard form :
y = −4(x + 1)(2x − 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 5x + 2x - 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 3x - 5)
y = −4(2x2 - 3x - 5)
y = −8x2 + 12x + 20
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling