ALTERNATE LIMIT DEFINITION OF DERIVATIVE
To find the derivative of the function f(x) at a point x = a, we will use the alternate limit definition.
Problem 1 :
The alternate definition of the derivative at the point x = a is
use the alternate definition to find f'(4) if f(x) = 8x - 7
Solution :
f(x) = 8x - 7
Here a = 4
f(4) = 8(4) - 7
= 32 - 7
= 25
Problem 2 :
Use the alternate definition to find f'(1) if f(x) = x3
Solution :
f(x) = x3
f(a) = a3
Here a = 1, then f(1) = 13 => 1
Problem 3 :
Use the alternate definition to find h'(2), where
h(x) = x3 + x2 - x
Solution :
h(x) = x3 + x2 - x
Here a = 2
h(2) = 23 + 22 - 2
= 8 + 4 - 2
= 12 - 2
h(2) = 10
h(x) - h(2) = x3 + x2 - x - 10
Using synthetic division, factoring the numerator.
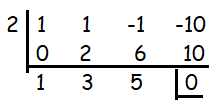
(x - 2)(x2 + 3x + 5)
Problem 4 :
Use the alternate definition to find f'(6), where
f(x) = 9x + 18
Solution :
f(x) = 9x + 18
Here x = 6
f(6) = 9(6) + 18
= 54 + 18
f(6) = 72
Problem 5 :
Use the alternate definition to find f'(-5), where
f(x) = -2x2 + 4x + 1
Solution :
f(x) = -2x2 + 4x + 1
Here a = -5
f(-5) = -2(-5)2 + 4(-5) + 1
= -2(25) - 20 + 1
= -50 - 20 + 1
f(-5) = -69
Applying x = -5, we get
= -2(-5-7)
= -2(-12)
= 24
Problem 6 :
Use the alternate limit definition to find g'(-2), if
g(x) = 6x2 - 8x + 3
Solution :
g(x) = 6x2 - 8x + 3
Here a = -2
f(-2) = 6(-2)2 - 8(-2) + 3
= 6(4) + 16 + 3
= 24 + 16 + 3
= 43
Recent Articles
-
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 PM
Finding Range of Values Inequality Problems -
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems
May 21, 24 08:51 AM
Solving Two Step Inequality Word Problems -
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling
May 20, 24 10:45 PM
Exponential Function Context and Data Modeling